Fix warnings generated by htmlCheck tox step. Change-Id: I82e14ae3327c64ff33d9b79df34bf80d66b8f9e3 Signed-off-by: Ron Stone <ronald.stone@windriver.com>
10 KiB
Example PTP Instance Configurations
The following sections provide example configuration steps for two configurations supported by .
- The first is a Border Clock setup where an external is providing a time source for the system. Only ptp4l and phc2sys are used for this configuration.
- The second shows how to setup a node when a time source is available
via a locally connected GNSS signal. The
ptp4l,phc2sys,ts2phcand clock instance types are used for this configuration.
Simple PTP configuration - T-BC
Using the topology shown, the following examples provide configurations for each service type:
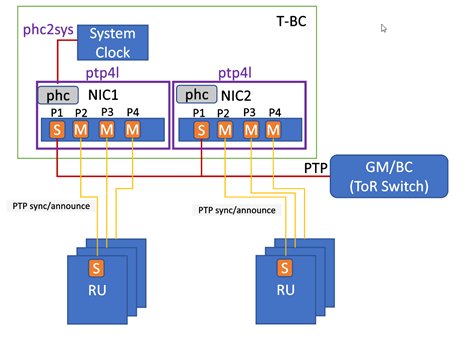
ptp4l
Create the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add ptp-inst1 ptp4lCreate a interface for the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add ptp-iface1 ptp-inst1Assign host interfaces to the interface.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if0 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if1 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if2 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if3 ptp-iface1Note
The
if0-if3field should be a name listed by thesystem host-if-list <hostname> -acommand.Additionally, assign ports for the second NIC.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if4 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if5 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if6 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if7 ptp-iface1Note
The
if0-if3field should be a name listed by thesystem host-if-list <hostname> -acommand.Add a parameter to the instance (e.g. domainNumber=24). Additional parameters can be added for other functionality.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add ptp-inst1 domainNumber=24Assign the instance to controller-0.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 ptp-inst1Apply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply
phc2sys
Create the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add phc-inst1 phc2sysCreate a interface for the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add phc-iface1 phc-inst1Assign host interface(s) to the interface.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if0 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if1 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if2 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if3 phc-iface1Note
The
if0-if3field should be a name listed by thesystem host-if-list <hostname> -acommand.Assign host interfaces from the second NIC.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if4 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if5 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if6 phc-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if7 phc-iface1Note
The
if0-if3field should be a name listed by thesystem host-if-list <hostname> -acommand.Add the required
uds_addressanddomainNumberparameters to the instance.~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add phc-inst1 uds_address=/var/run/ptp4l-ptp-inst1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add phc-inst1 domainNumber=24Note
The path assigned to
uds_addressmust use the name of theptp4linstance thatphc2sysis tracking.Assign the instance to controller-0.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 phc-inst1Apply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply
Alternate PTP configuration - T-GM
Using the topology shown, the following examples provide configurations for each service type.
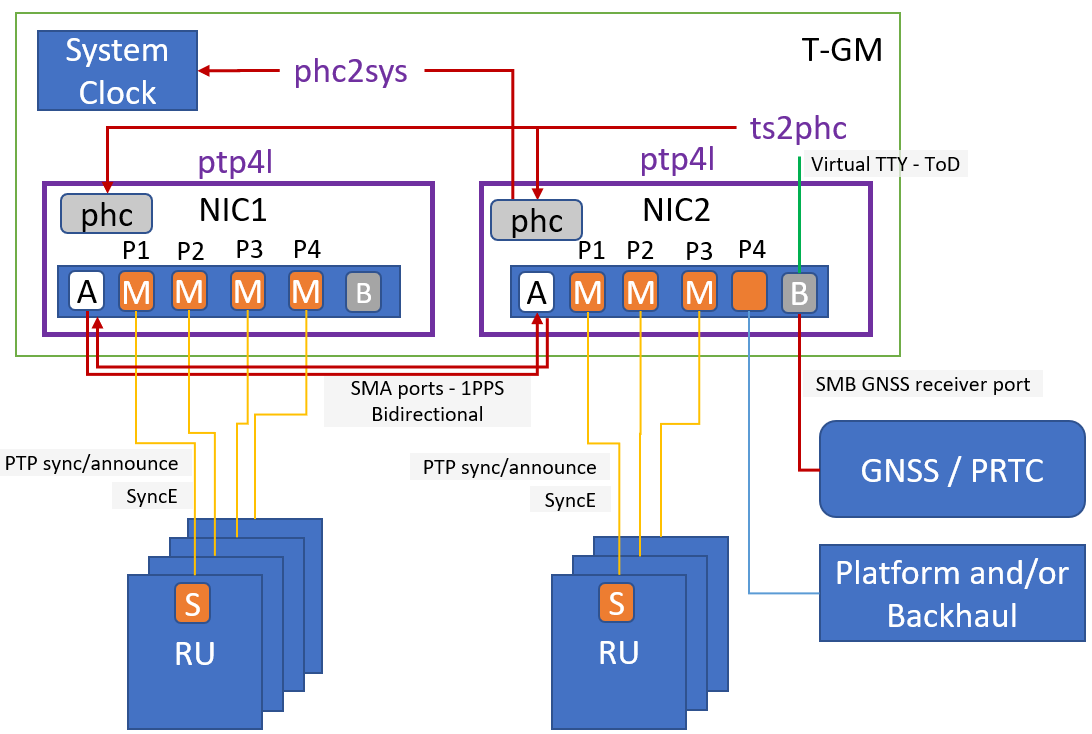
ts2phc
Create an instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add ts1 ts2phcCreate the interface and assign to ports.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add tsint1 ts1 # This is the port/PHC that we want to sync to GNSS time stamps, could be multiple PHCs if required ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 oam0 tsint1 # Assign a port on the second nic as well ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 data0 tsint1 This value is the path to the GNSS serial port that is connected, will vary system to system ~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add ts1 ts2phc.nmea_serialport=/dev/gnss0Additionally, find the NMEA serial port name of a given interface or NIC.
~(keystone_admin)]$ ls /sys/class/net/<network-interface>/device/gnss/For example, to find the NMEA serial port name of the enp81s0f0 interface:
~(keystone_admin)]$ ls /sys/class/net/enp81s0f0/device/gnss/Assign the instance to a host.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 ts1Apply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply
phc2sys
Add the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add phc-inst1 phc2sysUse the interface name that is being synced with
ts2phcabove.For example, if oam0 is on ens1f0, use ens1f0 below.
~(keystone_admin)]$ cmdline_opts='-w -s <port_name>'Add the required
uds_addressanddomainNumberparameters to the instance.$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add phc-inst1 uds_address=/var/run/ptp4l-ptp-inst1 $ system ptp-instance-parameter-add phc-inst1 domainNumber=24Note
The path assigned to uds_address must use the name of the ptp4l instance that phc2sys is tracking.
Assign the instance to a host.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 phc-inst1Apply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply
ptp4l
Note
You must create a second instance for the second NIC and repeat this process.
Create instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add ptp-inst1 ptp4lCreate an interface for the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add ptp-iface1 ptp-inst1Assign ports to the interface.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if0 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if1 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if2 ptp-iface1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 if3 ptp-iface1Add parameters to the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add ptp-inst1 domainNumber=24If configuring a node, set the special
ptp4lparametercurrentUtcOffsetValid=1.This allows the local clock and all downstream clocks to use the announced UTC offset.
$ system ptp-instance-parameter-add ptp-inst1 currentUtcOffsetValid=1Assign the instance to controller-0.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 ptp-inst1Apply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply
clock
Note
These parameters are used to enable the UFL/SMA ports, recovered clock syncE, and so-on. Refer to the user's guide for the Westport Channel or Logan Beach NIC for additional details on how to operate these cards.
The following parameters can be applied to the interface of a clock instance:
- sma1 input/output
- sma2 input/output
- u.fl1 output
- u.fl2 input
- synce_rclka enabled
- synce_rclkb enabled
Create the instance.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-add cl1 clockCreate a interface and assign host interfaces to it.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add clint1 cl1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 oam0 clint1The parameters are ultimately applied to the whole NIC, so adding multiple interface from the same NIC will override each other. The exception is the
synce_rclkparams, which are specific to the individual port.Add interface parameters.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-parameter-add clint1 sma1=output synce_rclka=enabledAssign the instance to a host.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-ptp-instance-assign controller-0 cl1Create a second clock interface to take input on the sma1 port in order to pass GNSS data to the second NIC.
Create a interface and assign host interfaces to it.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-add clint2 cl1 ~(keystone_admin)]$ system host-if-ptp-assign controller-0 data0 clint2Add interface parameters.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-interface-parameter-add clint2 sma1=input synce_rclka=enabledApply the configuration.
~(keystone_admin)]$ system ptp-instance-apply